Advantages of Carbon Fiber Electric Bikes In the quickly evolving world of electric bikes, a …
FAQ? What Makes the Motor Go?

Recent Posts
- Best Biking Cities in the USA for Electric Bicycles June 3, 2024
- Ride1Up Portola vs Aventon Sinch.2 Electric Bicycle May 26, 2024
- What’s a Dual Battery Electric Bicycle? April 29, 2024
- E-Bikes vs. Traditional Pedal: Which is Right For You? April 17, 2024
- Electric Dirt Bikes for BEGINNERS: Getting Started April 14, 2024
The Brains
The e-Bike Controller is one of the most significant components of an e-Bike. It essentially serves as the e-brain, assisting you in controlling all aspects of the the amount of assistance the motor provides. The controller allows you to regulate the power to the motor, the speed, acceleration, and more by connecting all of the electrical components of the e-Bike. This including the battery, motor, and throttle.
So, if you’re an e-Bike fan seeking to buy your first battery-powered bike, you should familiarize yourself with the many components of the controller to ensure a positive experience. Essentially, the controller is a little computer that serves as the “cerebral cortex”, allowing you to regulate the bike’s entire performance when power assist is needed or wanted form the motor.

How Controllers Work

An electric bike controller is a vital component that connects all of the bike’s electrical components in one location. Because they are exposed to the environment, controllers are usually packaged in a sealed protective box. Some designs, on the other hand, can be mounted inside the bike’s frame and hidden from view. The controller keeps track of the bike’s speed, acceleration, motor power, battery voltage, and pedaling activity, among other things. It also regulates the amount of pedal-assist you receive when riding your bike, based on the force on the pedals. You may control the amount of power transferred to the motor, which regulates the bike’s speed, by twisting the throttle as needed.
Speed and Voltage
The controller’s main job is to accept inputs from all of the electric components, such as the speed sensor, throttle, battery, display, and motor, and determine what to signal back. It also features a number of different protective functions that vary depending on the controller architecture. The following table lists the primary abilities the Controller in reference to protection.
Brake
Despite receiving other signals from the controller, the controller shuts down the motor during braking. When you apply the brakes and the throttle at the same time, the brake function takes precedence.
Over-Temperature
The controller also keeps an eye on the temperature of the Transistors, Resistors, Capacitors and Diods shutting off the motor if any of them get too hot. As a result, all of the electronic circuitry are safe from heat damage.
Over-Cut
If the current flowing to the motor is too high due to excessive resistance or load to the motor, the current going through the controller automatically decrease. This will safeguard both the motor and all of the electronic circuitry from failure.
Over-Voltage
The controller also keeps track of the battery voltage to prevent overcharging.
When the voltage is too high, it will shut down, ensuring that it is protected. When a battery is exposed to high voltage for an extended period of time, it can generate excessive heat, which might cause the battery to explode.
Low-Voltage
When the battery voltage falls below a certain threshold, the controller shuts down the motor. This protects the battery from being over-discharged. The design of rechargeable batteries allows them to cycle (recharge) multiple times. However, overcharging (drawing the battery to zero) can limit the number of cycles and battery life.
Different Types of Controllers
When selecting a controller for your e-Bike, make sure it is compatible with other bike components such as the motor, display, and battery. If you’re creating your own e-Bike, you’ll have to make this selection. If the e-Bike has already been designed, the manufacturer has already answered that question. Electric bike controllers can be classified based on a variety of factors. There are several key elements you should know whether you are a do-it-yourselfer or simply unbox, assemble, and ride person.
Sine or Square Wave
Sinewave (or Field Oriented Control FOC) controllers are often more expensive since producing a sine waveform to drive a motor efficiently demands a lot more computer resources. The computation of a square wave, on the other hand, is straightforward, requiring only the three phase on/off signal to run the motor in a time sequence.
The computation of a Square Wave, on the other hand, is straightforward, requiring only the three phase on/off signal to run the motor in a time sequence.
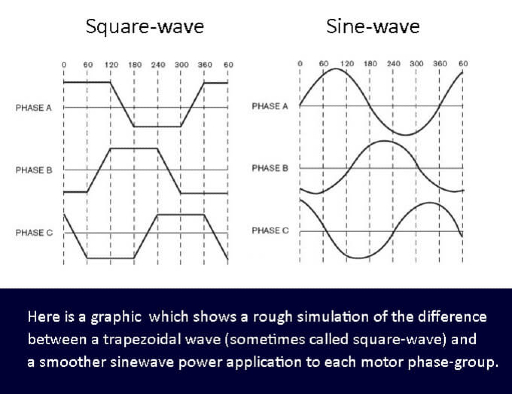
Sine wave controller advantage:
- lower noise and less heat.
- higher motor efficiency when climbing or with a heavy load.
- more efficient at lower speeds going up slopes.
- have a much smoother and more predictable control of all the operation.
Sine wave controller disadvantage:
- higher price.
- inefficient at high speeds.
- works with the matched motors only.
- higher power consumption.
Square wave controller advantage:
- lower price
- works with different motors.
- creates more power or torque when accelerating.
- higher efficiency at sudden accelerate or brake
- higher utilization of the power voltage
Square wave controller disadvantage:
- motor makes more noise.
- voltage sag at high speed may caue overheating or shutdown.
- the control is not linear, not smooth, and jerkey sometimes.
- lower motor efficiency when climbing or with a heavy load.
BLDC, Brushed or Brushless / DC
Permanent magnets and a collector are used in these motors. Their architecture is substantially simpler, consisting merely of a series of keys that control the current provided to the engine. Less current equates to less power, while higher current equates to more power. Other types of controllers exist, although they are rarely seen and are mostly utilized by extreme DIY hobbyists and enthusiasts. A BLDC or DC e-bike is the most common option for a regular person wishing to purchase an e-bike.
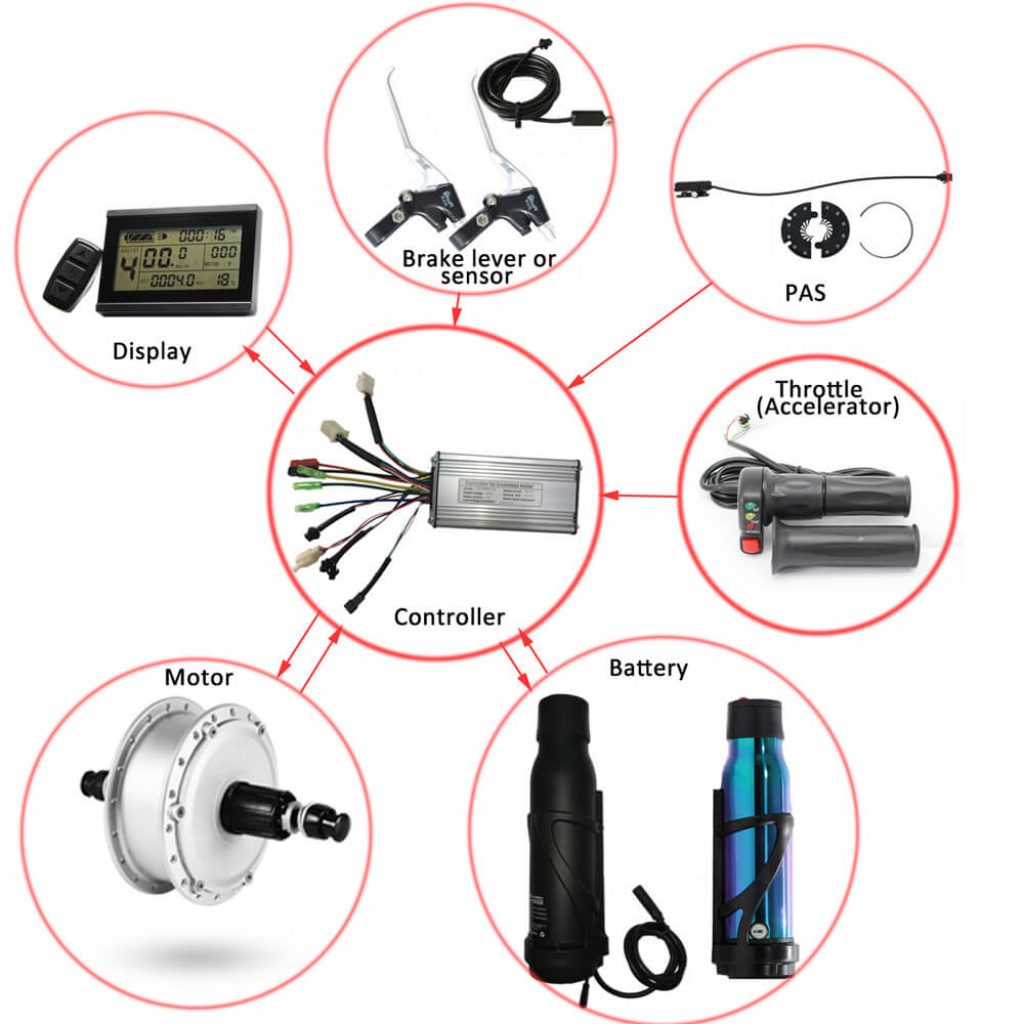


Hall Sensor or Dual Mode
If a motor has hall sensors, the controller should be hall-sensor or dual mode in most cases. The motor’s Hall sensor will detect rotation, and the controller will send the appropriate voltage to the motor based on the sensor readings. It’s more steady, uses less power, and has a higher starting torque. The Hall effect is used to create Hall sensors, which are relatively basic electronics. They determine the rotor’s position with relation to the stator. The rotor is the motor’s revolving component, whereas the stator is its stationary component. While a dual mode controller works well when the motor hall sensor is destroyed, the hall-sensor controller may prompt an error and stop working.
At the End of The Day...
There are currently a large number of controllers available in various configurations on the market. When it comes to purchasing a controller, don’t just order the first one you see on the internet; instead, take your time and thoroughly examine all of the features you’ll require. There are currently a large number of controllers available in various configurations on the market. When it comes to purchasing a controller, don’t just order the first one you see on the internet; instead, take your time and thoroughly examine all of the features you’ll require.
You might also like...
5 Best Mid-drive Electric Bikes in 2024 Electric bikes are the fastest-growing sector of bicycles, …
Electric Bike Motors What Makes a Bicycle an e-Bike? Electric Bike Motors If you’re thinking …
People one said that buggies would always be pulled by horses and bicycles would always be pushed by your legs. Well, that was 100 years ago and times have. EV Pedal Power is here to help you find that electric bicycle that fits your needs in the 21st century. With so many to choose from, our links are here to point you in the right direction.
EV Pedal Power participates in various affiliate marketing programs. We may get paid commissions on chosen products purchased through our links to merchant sites.




Recent Comments